President Biden: Reining in the Supreme Court or Shaping His Presidential Legacy?
Proposes to Whittle Down Presidential Immunity Fortified by the Recent Supreme Court Judgement.
Proposing Far-reaching Constitutional Amendments
In a significant shift in focus within the Democratic Party’s campaign, President Joe Biden is striving to establish a lasting legacy in U.S. politics. While Vice President Kamala Harris garners increasing attention, President Biden tweeted on Monday evening (29th July) his resolve to initiate a critical debate to strengthen American democracy. He proposed far-reaching reforms to the terms and conditions of Supreme Court justices' appointments, who are currently appointed for life. In his statement, he emphasized, "We can and must prevent the abuse of presidential power. We can and must restore the public’s faith in the Supreme Court. We can and must strengthen the guardrails of democracy."
As he continues to lead the nation until January 2025, when a new President will be sworn in, Biden has put forth three bold reforms. These reforms aim to restore trust and accountability within the Supreme Court and the broader democratic framework of the United States.
1.) No One Is Above the Law Amendment
President Biden is advocating for a constitutional amendment named the "No One Is Above the Law Amendment." This amendment seeks to unequivocally affirm that former presidents cannot claim immunity for crimes committed while in office. Reflecting the Founders' belief in the limitations of presidential power, this reform reinforces the principle that the United States is governed by laws rather than by the whims of kings or dictators. This initiative comes in the wake of the recent Supreme Court verdict in the case of Donald Trump, where the apex court held that there was absolute immunity against prosecution for decisions pertaining to core government functions taken by the President while in office.
2.) Term Limits for Supreme Court Justices
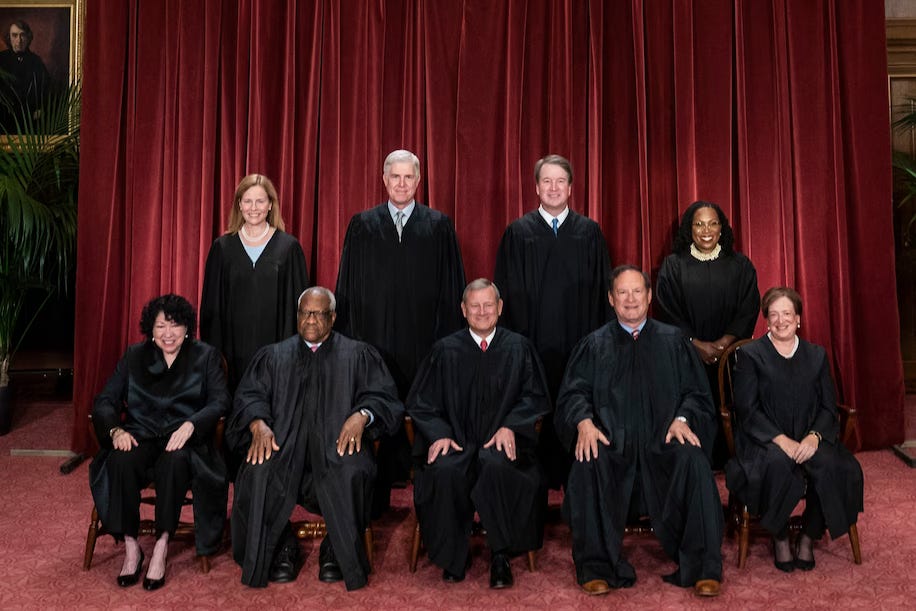
President Biden is calling for the introduction of term limits for Supreme Court justices, similar to the term limits imposed on U.S. presidents for nearly 75 years. The United States stands alone among major constitutional democracies in granting lifetime appointments to its apex court. By implementing term limits, Biden aims to ensure regular changes in the court's membership, making the timing of court nominations more predictable and less arbitrary. This reform is designed to prevent any single presidency from exerting an outsized influence on the court's composition for generations to come. Biden envisions a system where each president would appoint a justice every two years, with each justice serving an 18-year term on the Supreme Court. Currently, of the nine justices holding office, six were appointed by Republican presidents and three by Democratic presidents. Although their decisions are theoretically independent, they often reflect ideological lines corresponding to the political parties that appointed them.
3.) Binding Code of Conduct for the Supreme Court
President Biden is pushing for the establishment of a binding code of conduct for the Supreme Court. Currently, the court operates under a voluntary ethics code that is both weak and self-enforced. Biden argues that justices should be mandated to disclose gifts, refrain from public political activities, and recuse themselves from cases where they or their spouses have financial or other conflicts of interest. This proposed binding code of conduct would align the Supreme Court with the standards expected of all other federal judges, who are already subject to enforceable ethical guidelines. This initiative is perhaps triggered by allegations that some sitting judges have received undue favours from private individuals, including personal friends, such as free holidays and trips in private jets.
Pros and Cons of the Proposed Reforms
Pros:
Enhancement of Accountability: The "No One Is Above the Law Amendment" would reinforce the accountability of former presidents, ensuring they can be prosecuted for crimes committed while in office.
Regular Court Renewal: Implementing term limits for Supreme Court Justices would foster regular updates to the court’s composition, promoting a dynamic and contemporary judicial body reflective of evolving societal values.
Ethical Integrity: A binding code of conduct would enhance the ethical standards of the Supreme Court, promoting greater transparency and trust in the judiciary.
Cons:
Constitutional Amendment Challenges: Passing a constitutional amendment is a complex and arduous process (details below) requiring significant political consensus, which may be difficult to achieve.
Potential Politicization: Term limits could lead to increased politicization of the Supreme Court appointment process, with more frequent nominations possibly heightening partisan tensions.
Judicial Independence Concerns: Critics may argue that a binding code of conduct could impinge on judicial independence, potentially subjecting justices to undue scrutiny and pressure.
The Challenge of Constitutional Amendments
Amending the United States Constitution is an arduous process, requiring a significant consensus across the political spectrum. Since its inception, only 27 amendments have been ratified, including the initial ten amendments known as the Bill of Rights, which were adopted shortly after the Constitution was written. Following the Civil War, notable amendments such as the 13th, 14th, and 15th were added to abolish slavery and establish civil rights.
a.) Historical Context and Key Amendments
Since its inception, only 27 amendments have been ratified, including the initial ten amendments known as the Bill of Rights, which were adopted shortly after the Constitution was written. Following the Civil War, notable amendments such as the 13th, 14th, and 15th were added to abolish slavery and establish civil rights.
b.) Rigorous Procedure for Amendment
The procedure for amending the Constitution is intentionally rigorous to ensure broad support and careful consideration. An amendment can be proposed either by a two-thirds majority in both the House of Representatives and the Senate or by a constitutional convention called for by two-thirds of state legislatures. Once proposed, it must then be ratified by three-fourths of the state legislatures or by conventions in three-fourths of the states. This complex and demanding process ensures that only amendments with widespread approval become part of the Constitution.
Fortifying American Democracy
President Biden’s proposed reforms aim to fortify the foundations of American democracy by ensuring that no individual, regardless of their position, is above the law. These changes seek to introduce regular renewal within the Supreme Court and uphold the highest ethical standards for its justices. While the path to implementing these reforms may be fraught with challenges, the potential benefits of increased accountability, transparency, and integrity within the judiciary are profound. The commitment to these principles reflects a genuine attempt to strengthen American democracy through systemic changes that promote fairness and justice.
Political Implications and Legacy
While Biden's initiative to introduce these amendments, or at least trigger a debate, comes at the height of the presidential electoral campaign, the political implications are not lost on observers. Many see this as a strategic move within the context of the election, especially considering that two of the four criminal indictments against Trump may be influenced by the Supreme Court’s decision on presidential immunity. Additionally, it sends a broad message to the electorate that several progressive and people-friendly reforms of the Democratic Party have been obstructed by Supreme Court judgments, often split 6-3 along ideological lines. In championing these reforms, Biden aspires to leave a lasting legacy that underscores the enduring principle that in America, the people rule. However, the impact on the political fortunes of Donald Trump and Kamala Harris remains to be seen.